Oil & Gas
Decarbonisation
CTS supports the decarbonisation of the oil and gas sector by powering operations from sustainable energy sources.
Europe-wide offshore oil and gas industry targets are 50% CO2 reduction by 2030 and achieving net zero by 2050.

Electricifcation of the North Sea
Orcadian Energy, 2022
In Europe, governments have given oil and gas companies targets for decarbonising power supply for offshore production platforms.
In the UK sector of the North Sea, all but a few offshore production platforms are decades old, are congested with equipment and are well-progressed through their field life. Modifications at this stage are complex and most often expensive. This limits the allowance for new equipment, and further modifications are a significant challenge.
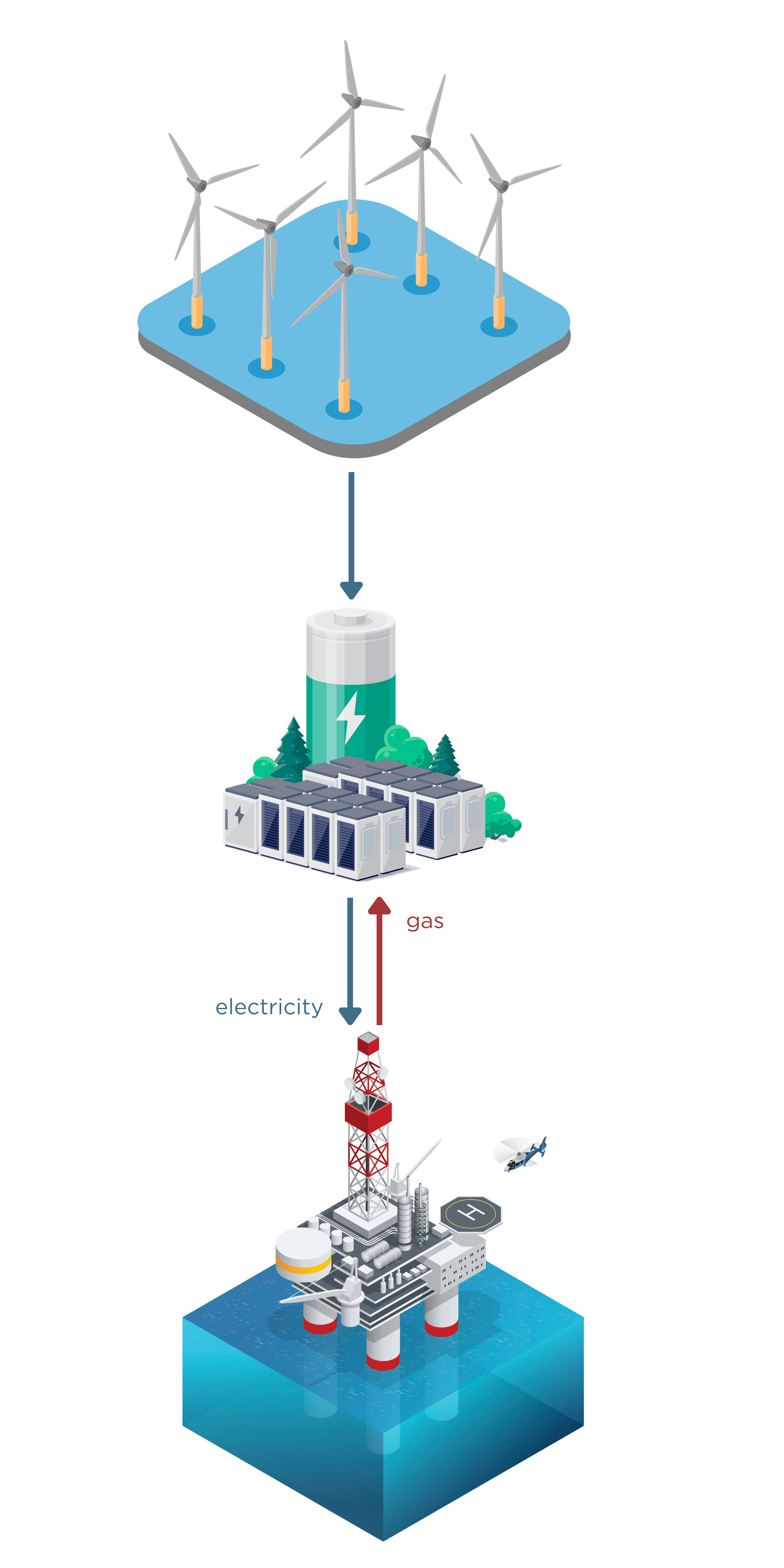
While working with partners, we proposed a microgrid concept for a low-carbon, reliable off-grid option for powering North Sea platforms. CTS cable solution is a key enabling technology to develop future offshore microgrids to supply platforms by low carbon sources.
Analysis indicates that emissions will be reduced by up to 80% against today’s numbers, and the cost for power delivery will be 25% lower than if powered from the shore.
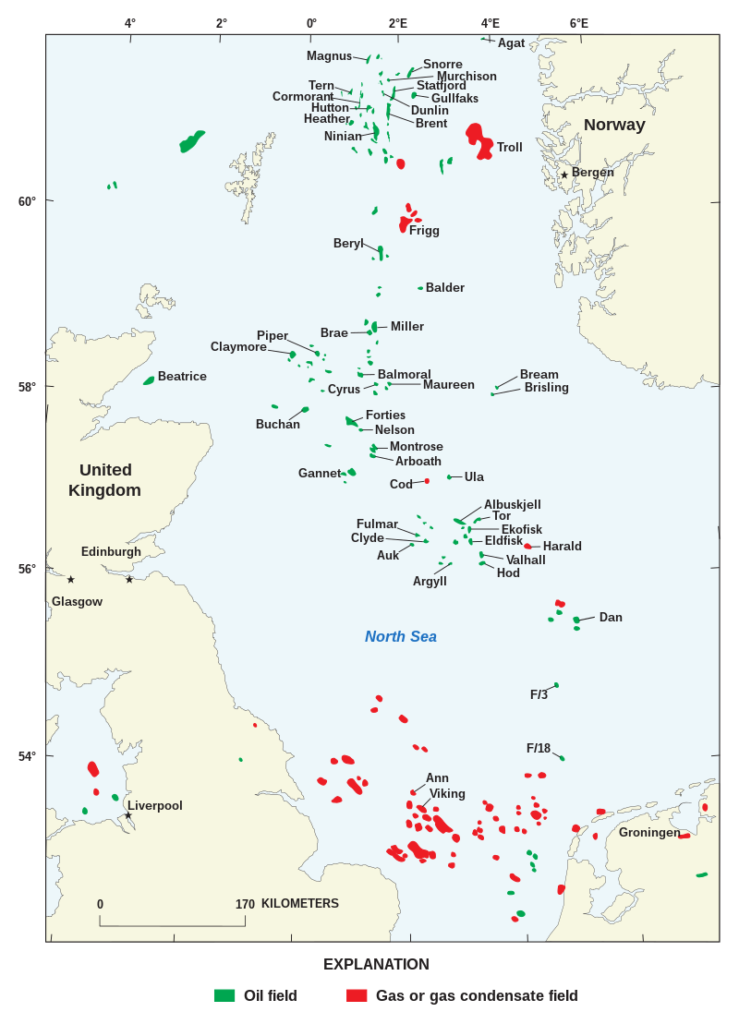
Map of North Sea Oil & Gas fields
Benefits of CTS for Oil & Gas
CTS has a significantly lower voltage drop along its length, allowing connections with greater distances and potentially lower transmission voltage or with less copper.
Operation of the cable at lower voltages and elimination of additional compensation allows lighter equipment requirements on the existing platform, reducing the transition costs of decarbonisation.
CTS-enabled offshore AC systems are also more flexible and enable the creation of an offshore network connected to shore or operated as an island mini-grid.
Lower use of copper and other materials preserves the environment that could be damaged by mining and processing of minerals.
CTS cable is a self-compensating cable that reduces or eliminates the requirement to cope with the large reactive power load when using a large percentage of rotating power equipment.
Offshore CTS cable can cost-effectively deliver power by AC, avoiding more expensive DC systems and challenging-to-maintain HVDC converters.
CTS cable can deliver the same power through a smaller cross-section than conventional cable, reducing cable costs and CO2 emissions by up to 30%.
Three Components of the Microgrid Concept
- Wind farms distributed around platforms
- Distribution hubs collecting AC power from the wind farms and energy-efficient gas-fired engines operated when the wind is low
- A network of CTS cables to deliver power from wind farms to the operators’ platforms